Debt Payments to Income Ratio
Understanding your debt payments to income ratio is crucial for financial health. This metric shows how much of your income goes to paying debts.
Managing finances can be challenging, especially with multiple debts. But knowing your debt payments to income ratio can help. It tells you if your debt level is manageable or too high. This ratio is vital for budgeting, planning, and even securing loans.
It acts as a snapshot of your financial stability. By keeping this ratio in check, you can make informed decisions and avoid financial stress. Stay tuned as we dive deeper into how to calculate and improve your debt payments to income ratio.
Introduction To Debt Payments To Income Ratio
Debt Payments to Income Ratio measures the percentage of your income used to pay debts. It helps assess financial health and borrowing capacity. Lower ratios indicate better financial stability.
Understanding your financial health is crucial. One key metric is the Debt Payments to Income Ratio. This ratio helps you see how much of your income goes to debt payments. It is a useful tool for managing your finances.
Importance Of Financial Ratios
Financial ratios give you a clear picture of your financial status. They help you make informed decisions. The Debt Payments to Income Ratio is one such important ratio. It shows if you are overburdened with debt. Lenders also use this ratio to assess your credit risk.
Basic Concept
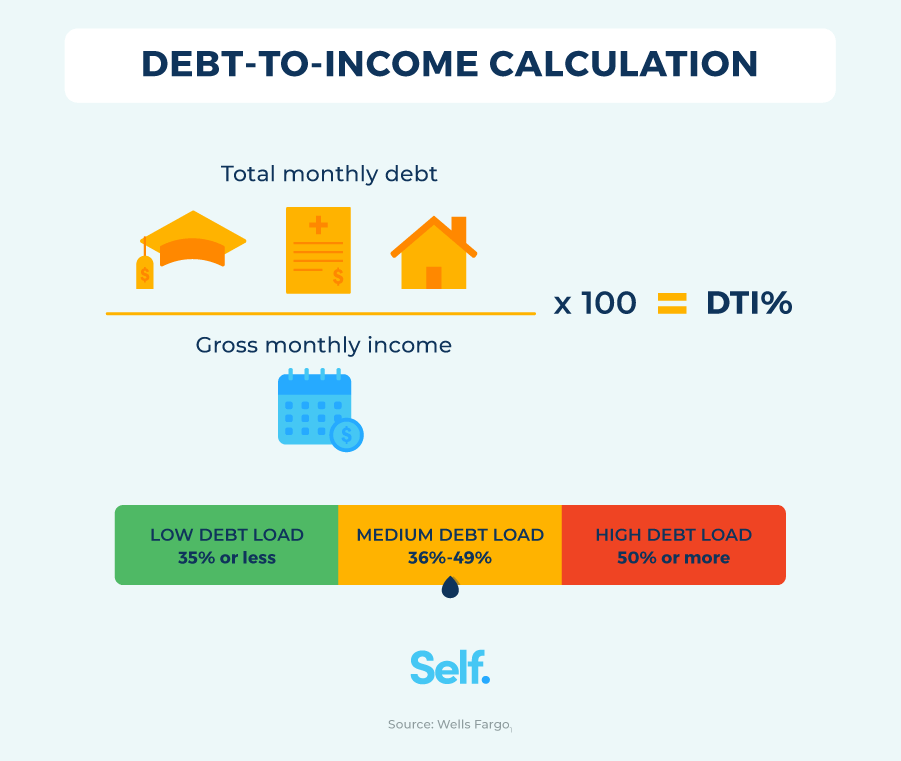
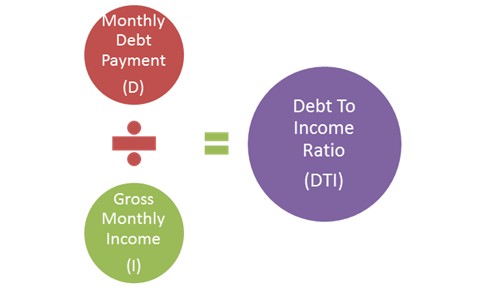
The Debt Payments to Income Ratio is simple to understand. It is the percentage of your income that goes to debt payments. To calculate, divide your monthly debt payments by your monthly income. Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage. A lower ratio means better financial health. It indicates you have more income left after paying debts. A higher ratio can signal financial stress. It means a significant portion of your income goes to debt. “`
Calculating Your Debt Payments To Income Ratio
The Debt Payments to Income Ratio (DPIR) is a key metric for understanding your financial health. Calculating this ratio helps determine how much of your income goes towards paying debt. A lower ratio indicates a healthier financial situation. Let’s delve into how to calculate your DPIR.
Required Information
To calculate your Debt Payments to Income Ratio, gather the following details:
- Total monthly debt payments
- Gross monthly income
Total monthly debt payments include all monthly payments towards loans, credit cards, and other debts. Your gross monthly income is your income before taxes and other deductions.
Step-by-step Calculation
Follow these steps to calculate your Debt Payments to Income Ratio:
- Sum all your monthly debt payments.
- Calculate your gross monthly income.
- Divide the total monthly debt payments by the gross monthly income.
- Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage.
Here is the formula:
DPIR = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100For example, if your total monthly debt payments are $1,500 and your gross monthly income is $5,000, your DPIR calculation will be:
DPIR = ($1,500 / $5,000) x 100 = 30%This means 30% of your income goes towards debt payments. Regularly calculating your Debt Payments to Income Ratio can help manage your finances better. Keep your DPIR below 36% for optimal financial health.
Debt-to-Income Ratio Calculator
Interpreting Your Ratio
Understanding your debt payments to income ratio is crucial. This ratio shows how much of your income goes towards paying off debt. A better understanding can help you manage finances better.
Ideal Ratios
Experts suggest an ideal debt-to-income ratio should be below 36%. Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Ratio | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| < 20% | Excellent. Manageable debt levels. |
| 20%-36% | Good. Debt is under control. |
| > 36% | Risky. Might struggle with debt. |
What High And Low Ratios Indicate
A high debt-to-income ratio means more of your income goes to debt. This can lead to financial stress. You may find it hard to save or handle emergencies. A low debt-to-income ratio is a sign of financial health. It means you have more income available for savings and other expenses. You can manage debt better. Understanding your debt payments to income ratio can help you make better financial decisions. It can guide you in reducing debt and improving your financial situation.

Impact On Financial Health
The Debt Payments to Income Ratio (DTI) is crucial for your financial health. It shows how much of your income goes to paying debt. A high DTI ratio can harm your financial well-being. It can affect your ability to save, invest, and get credit.
Savings And Investments
High DTI means less money for savings and investments. If a large part of your income goes to debt, you have less to save. This can hinder your financial growth. Example:
| Income | Debt Payments | Money for Savings |
|---|---|---|
| $5,000 | $2,000 | $3,000 |
| $5,000 | $3,500 | $1,500 |
In the second case, high debt payments reduce the amount for savings. Less savings can mean fewer investment opportunities.
Creditworthiness
Your DTI ratio impacts your creditworthiness. Lenders check this ratio to decide if you are a good borrower. A high DTI suggests you have too much debt. This can make it hard to get loans or credit cards. Key Points:
- High DTI can lead to loan rejections.
- It can result in higher interest rates.
- Low DTI improves your chances of getting credit.
Maintaining a low DTI ratio helps you stay financially healthy. It ensures you have enough money for savings and investments. It also improves your creditworthiness. Keep your DTI ratio low to secure your financial future.
Strategies To Improve Your Ratio
Improving your Debt Payments to Income Ratio (DTI) can ease financial stress. A better ratio means you have more money to save or spend. Here are some strategies to help improve your DTI ratio.
Debt Repayment Plans
Creating a structured debt repayment plan can help you manage your debts better. There are several methods to consider:
- Debt Snowball Method: Focus on paying off the smallest debts first. Once a debt is paid off, move to the next smallest. This gives a sense of achievement and momentum.
- Debt Avalanche Method: Pay off debts with the highest interest rates first. This can save money on interest in the long run.
- Debt Consolidation: Combine all your debts into one loan. This can result in a lower interest rate and a single monthly payment.
Choose a method that suits your financial situation and personality. Sticking to a plan can lower your DTI ratio over time.
Increasing Income
Boosting your income can improve your DTI ratio. Here are a few ways to increase your earnings:
- Part-time Jobs: Consider taking a part-time job or freelance work. This extra income can go directly towards debt payments.
- Sell Unused Items: Sell items you no longer need. Use this money to pay off debts.
- Ask for a Raise: If you have been in your job for a while, ask for a raise. Highlight your achievements and contributions to justify the request.
- Learn New Skills: Invest in learning new skills that can lead to higher-paying jobs. Online courses and certifications can be valuable.
By increasing your income, you can pay off debts faster and improve your DTI ratio.
Tools And Resources
Managing your Debt Payments to Income Ratio can be challenging. Thankfully, there are many tools and resources available to help. These can simplify the process and provide you with a clear understanding of your financial situation. This section covers some of the most useful tools and resources.
Online Calculators
Online calculators are a great starting point. They are easy to use and can quickly provide you with important information. Many websites offer free calculators that can compute your Debt Payments to Income Ratio. Simply enter your monthly income and debt payments. The calculator will do the rest. Some popular options include:
- Bankrate – Offers a comprehensive debt-to-income calculator.
- NerdWallet – Provides a user-friendly interface for quick calculations.
- Mortgage Calculators – Focuses on home loans and related debts.
Financial Advisors
Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized guidance. They can help you understand your Debt Payments to Income Ratio and offer strategies to improve it. Financial advisors can also assist in creating a budget and setting financial goals. Benefits of working with a financial advisor:
- Personalized Advice – Tailored to your specific financial situation.
- Long-term Planning – Helps you plan for future financial stability.
- Accountability – Keeps you on track with your financial goals.
Finding a trusted financial advisor is important. You can search for certified professionals through organizations like the Certified Financial Planner Board or National Association of Personal Financial Advisors. Using these tools and resources can make managing your Debt Payments to Income Ratio easier and more effective. Whether you prefer online calculators or professional advice, there are many options to suit your needs.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Overlooking Small Debts
Small debts might seem insignificant. But they can accumulate quickly. Ignoring them can lead to financial trouble. Keep track of every small debt. Use a spreadsheet or a budgeting app. This helps you stay aware of your total debt. Even a small loan can have high interest. This increases your debt over time. Prioritize paying off these small debts first.Ignoring Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in your debt. High-interest rates mean you pay more over time. Compare interest rates before borrowing. Choose loans with the lowest interest. This saves you money in the long run. Refinance high-interest loans if possible. Lowering your interest rate can reduce your monthly payments. Here’s a simple table to illustrate the impact of interest rates:| Loan Amount | Interest Rate | Monthly Payment | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| $5,000 | 5% | $95 | $5,700 |
| $5,000 | 15% | $120 | $7,200 |
Long-term Financial Planning
Planning for the long term is crucial for financial stability. One key aspect is understanding your debt payments to income ratio. This ratio helps you manage debt while achieving financial goals. Here, we will discuss the importance of building an emergency fund and retirement planning.
Building An Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is a financial safety net. It covers unexpected expenses like medical bills or car repairs. Aim to save at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses. Here is a simple table to guide you:
| Monthly Expenses | Emergency Fund Goal (3 months) | Emergency Fund Goal (6 months) |
|---|---|---|
| $1,000 | $3,000 | $6,000 |
| $2,000 | $6,000 | $12,000 |
| $3,000 | $9,000 | $18,000 |
Automate your savings. Set up a direct transfer from your paycheck. This makes saving easier and more consistent.
Retirement Planning
Retirement planning ensures a comfortable life post-retirement. Start by calculating how much you need. Consider factors like living expenses, healthcare, and lifestyle. Use this checklist:
- Estimate monthly expenses in retirement
- Calculate expected retirement income
- Identify gaps between income and expenses
- Set savings goals to cover the gaps
- Invest in retirement accounts like 401(k) or IRA
Start saving early. The sooner you start, the more you benefit from compound interest. Review your plan regularly. Adjust for changes in income, expenses, or goals. Remember, a solid long-term plan helps reduce stress. It ensures financial stability and peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Debt Payments To Income Ratio?
Debt Payments to Income Ratio measures your monthly debt payments against your monthly income. It helps assess financial health.
How To Calculate Debt Payments To Income Ratio?
Divide total monthly debt payments by gross monthly income. Multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
Why Is Debt Payments To Income Ratio Important?
It indicates your ability to manage debt. Lenders use it to evaluate loan eligibility.
What Is A Good Debt Payments To Income Ratio?
A ratio below 36% is generally considered good. It shows manageable debt levels.
Conclusion
Understanding your debt payments to income ratio is crucial. It helps manage finances better. Keep your ratio low to stay financially healthy. Regularly review your expenses and income. Make adjustments as needed. A balanced ratio ensures less stress. It also improves your credit score.
Stay informed and stay in control. Prioritize paying off high-interest debts first. This approach saves money in the long run. Remember, financial health starts with informed decisions.







